Creating Sessions
When building automation workflows, you often need to maintain browser state across multiple connections such as keeping a user logged in, preserving shopping cart contents, or maintaining form data between script runs. Browserless provides two distinct approaches for creating persistent browser sessions that survive disconnections and allow you to resume automation from where you left off.
Session Management Approaches
Browserless offers two methods for managing persistent browser sessions:
1. Browser Sessions - Use the Browserless.reconnect CDP command to maintain state between connections. This approach works with all automation libraries and automatically manages session lifecycle through browser process persistence.
2. Session API - Provides explicit programmatic control over session creation and deletion through dedicated REST endpoints. This approach is designed for advanced use cases requiring precise lifecycle management or integration with larger automation platforms.
Which approach to use
Use Browser Sessions When:
- Working with existing automation scripts
- Need simple session persistence with minimal setup
- Want maximum compatibility across automation libraries
- Session lifetime is managed by your application logic
- You prefer CDP-based session management
Use Session API When:
-
Needs a dedicated user data directory per session, persisting cache, cookies, localStorage, and session data for multiple days
-
Need explicit session lifecycle control through HTTP endpoints
-
Building advanced session management workflows
-
Want programmatic session creation/deletion capabilities
-
Need session monitoring and metadata access
-
Integrating with larger automation platforms or microservices
Pseudocode workflow diagram
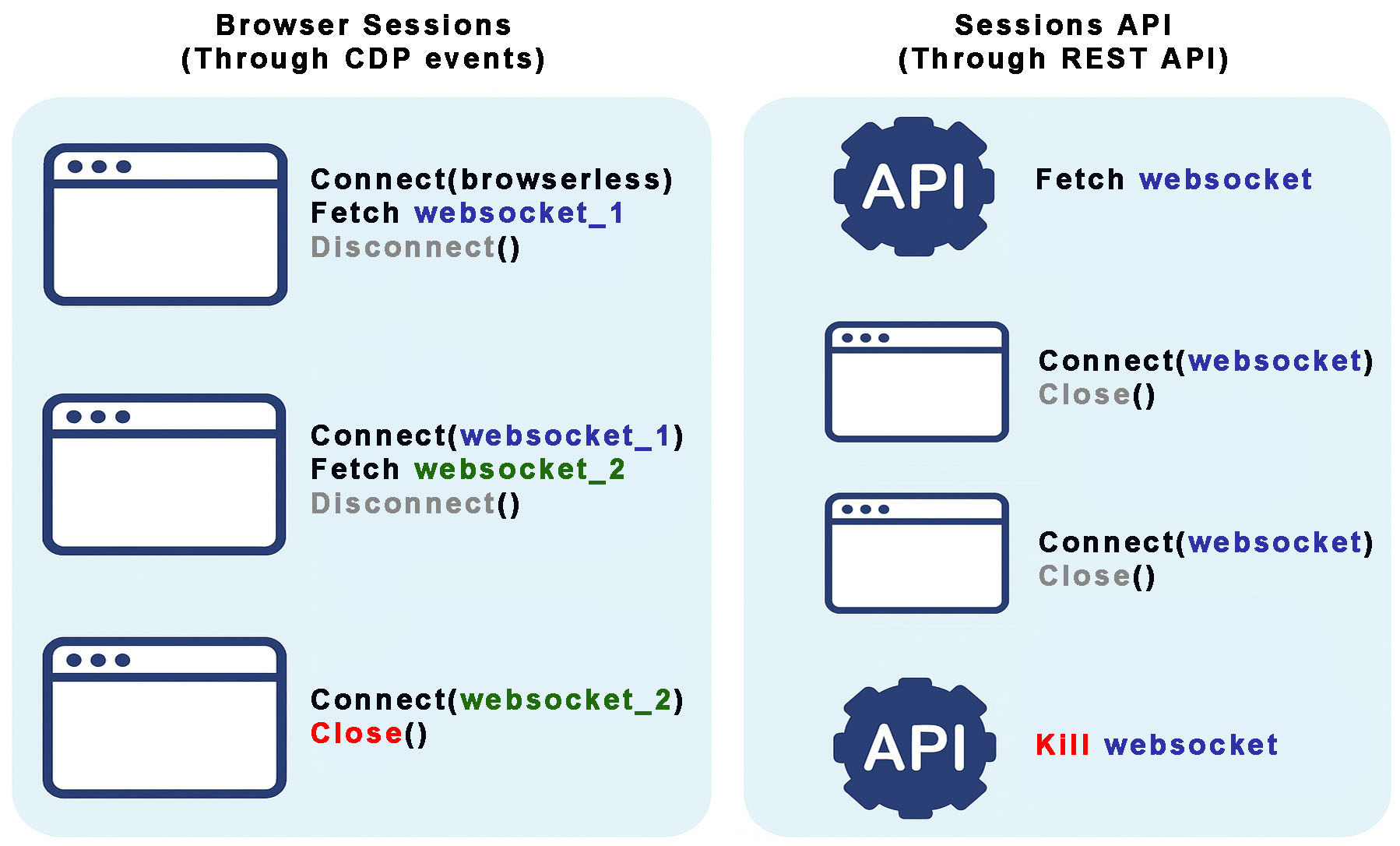
Browser Sessions
The standard approach uses the Browserless.reconnect CDP command to generate a browserWSEndpoint to reuse later on, which keeps the browsers alive after disconnection for a specified timeout duration.
How Reconnection Works
When you use the Browserless.reconnect command, Browserless:
- Keeps the browser alive for the specified reconnection timeout duration after you disconnect
- Maintains browser state including cookies, localStorage, sessionStorage, and cache
- Allows reconnection to the same browser instance within the reconnection timeout window
- Automatically cleans up the browser instance after the reconnection timeout expires
Important: The browser session itself can run for the full session duration (15-60 minutes), but once you disconnect after using reconnect, you have a limited time window to reconnect to that specific browser instance. It's critical to note that the browser will be closed down if the browser.close() method is used, so you'll need to use the browser.disconnect() method so that the browser is kept alive for reconnection.
Browser Sessions Reconnection TTL Limitations by Plan
Reconnection TTL (Time-To-Live) is the maximum duration that a browser instance remains alive and available for reconnection after you disconnect from it using Browserless.reconnect. This is a reconnection window, not your overall session timeout.
Key distinctions:
- Reconnection TTL: How long the browser waits for you to reconnect after using
Browserless.reconnectand disconnecting (10 seconds to 5 minutes depending on plan) - Overall Session Timeout: Total time your browser session can run continuously (15-60 minutes depending on plan)
- Reconnection Window: The specific time period during which you can reconnect to the same browser instance
If you don't reconnect within the TTL window, that specific browser instance closes, but you can always start a new session.
The reconnection Time-To-Live duration is 30 seconds (30,000ms) by default, but can be increased depending on your plan type.
| Plan | Maximum Reconnection TTL | Overall Session Timeout |
|---|---|---|
| Free | 10 seconds (10,000ms) | 60 seconds |
| Prototyping/Starter | 1 minute (60,000ms) | 15-30 minutes |
| Scale | 5 minutes (300,000ms) | 60 minutes |
Creating a Session
- Puppeteer
- Playwright
import puppeteer from "puppeteer-core";
// Connect to browser with your API token
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: "wss://production-sfo.browserless.io?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN",
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
const cdp = await page.createCDPSession(); // Create CDP session for reconnection
await page.goto("https://example.com");
// Set up session state that will persist across reconnections
await page.evaluate(() => {
localStorage.setItem("myData", "persistent-value");
});
// Enable reconnection with 60 second timeout (must be within plan limits)
const { error, browserWSEndpoint } = await cdp.send("Browserless.reconnect", {
timeout: 60000, // Browser stays alive for 60 seconds after disconnect
});
if (error) throw error;
console.log("Reconnection endpoint:", browserWSEndpoint);
// Use disconnect() instead of close() to keep browser alive for reconnection
await browser.disconnect(); // Browser remains alive for 60 seconds
import { chromium } from "playwright";
// Connect to browser with your API token
const browser = await chromium.connectOverCDP(
"wss://production-sfo.browserless.io?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN",
);
const page = await browser.newPage();
const cdpSession = await page.context().newCDPSession(page); // Create CDP session for reconnection
await page.goto("https://example.com");
// Set up session state that will persist across reconnections
await page.evaluate(() => {
localStorage.setItem("myData", "persistent-value");
});
// Enable reconnection with 60 second timeout (must be within plan limits)
const { error, browserWSEndpoint } = await cdpSession.send(
"Browserless.reconnect",
{
timeout: 60000, // Browser stays alive for 60 seconds after disconnect
},
);
if (error) throw new Error(error);
console.log("Reconnection endpoint:", browserWSEndpoint);
// Use disconnect() instead of close() to keep browser alive for reconnection
await browser.disconnect(); // Browser remains alive for 60 seconds
Session Configuration
You can combine reconnection timeouts with other browser options for advanced configuration:
// Configure browser with launch parameters that will persist across reconnections
const queryParams = new URLSearchParams({
token: "YOUR_API_TOKEN",
stealth: true, // Enable stealth mode for bot detection bypass
proxy: "residential", // Use residential proxy
headless: false, // Run in headed mode for debugging
});
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: `wss://production-sfo.browserless.io?${queryParams.toString()}`,
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
const cdp = await page.createCDPSession(); // Create CDP session for reconnection
// Enable reconnection with all launch options preserved
const { error, browserWSEndpoint } = await cdp.send("Browserless.reconnect", {
timeout: 60000, // All configured options remain active after reconnection
});
Session API
For more control over session lifecycle, you can use the REST API to explicitly create and manage sessions through HTTP endpoints. This approach provides programmatic session management with advanced control over session configuration and monitoring.
Creating a Session via REST API
- JavaScript
- Python
- cURL
// Configure session with explicit timeout and browser options
const sessionConfig = {
ttl: 180000, // Session timeout: 3 minutes (180,000ms)
stealth: true, // Enable stealth mode for bot detection bypass
headless: false, // Run in headed mode for debugging
args: [
"--no-sandbox", // Required for containerized environments
"--disable-dev-shm-usage", // Prevent shared memory issues
"--disable-background-timer-throttling", // Maintain performance
],
};
// Create session via REST API
const response = await fetch(
"https://production-sfo.browserless.io/session?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN",
{
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify(sessionConfig),
},
);
// Handle session creation errors
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(
`Failed to create session: ${response.status} "${await response.text()}"`,
);
}
// Extract WebSocket connection URL for automation libraries
const session = await response.json();
console.log("Session created, browserWSEndpoint:", session.connect);
import requests
# Configure session with explicit timeout and browser options
session_config = {
'ttl': 180000, # Session timeout: 3 minutes (180,000ms)
'stealth': True, # Enable stealth mode for bot detection bypass
'headless': False, # Run in headed mode for debugging
'args': [
'--no-sandbox', # Required for containerized environments
'--disable-dev-shm-usage', # Prevent shared memory issues
'--disable-background-timer-throttling', # Maintain performance
]
}
# Create session via REST API
response = requests.post(
'https://production-sfo.browserless.io/session',
params={'token': 'YOUR_API_TOKEN'},
json=session_config
)
# Extract WebSocket connection URL for automation libraries
session_data = response.json()
print(f'Session created: {session_data["connect"]}')
# Create session via REST API with configuration
curl -X POST "https://production-sfo.browserless.io/session?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"ttl": 180000,
"stealth": true,
"headless": false,
"args": [
"--no-sandbox",
"--disable-dev-shm-usage",
"--disable-background-timer-throttling"
]
}'
# Response includes "connect" field with WebSocket URL for automation libraries
Session Configuration Options
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ttl | number | 300000 | Time-to-live in milliseconds (max 30 minutes) |
stealth | boolean | false | Enable stealth mode to avoid detection |
headless | boolean | true | Run browser in headless mode |
args | string[] | [] | Additional Chrome launch arguments |
proxy | object | null | Proxy configuration |
Connecting to Session API
After creating a session with the Session API, use the returned connect URL to connect your automation library to the persistent session:
- Puppeteer
- Playwright
- Python
import puppeteer from "puppeteer-core";
// Use the WebSocket URL returned from session creation
const connect =
"wss://production-sfo.browserless.io/e/53...21/session/connect/b9..7b?token=25df...";
// Connect to the existing session
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: connect,
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto("https://example.com");
console.log(await page.url());
// Check if session state persists from previous connections
const foo = await page.evaluate(() => {
return window.localStorage.getItem("foo");
});
if (foo) {
console.log("LocalStorage foo exists:", foo); // State persisted
} else {
console.log("LocalStorage foo does not exist, this is the first run");
}
// Session state is maintained by the Session API across connections
await page.evaluate(() => {
localStorage.setItem("foo", "bar"); // This will persist for future connections
});
// Session remains active even after closing browser connection
await browser.close(); // Session continues running until TTL expires
import { chromium } from "playwright-core";
// Use the WebSocket URL returned from session creation
const connect =
"wss://production-sfo.browserless.io/e/53...21/session/connect/b9..7b?token=25df...";
// Connect to the existing session
const browser = await chromium.connectOverCDP(connect);
const context = browser.contexts()[0]; // Use existing browser context
const page = await context.newPage();
await page.goto("https://example.com");
console.log(await page.url());
// Check if session state persists from previous connections
const foo = await page.evaluate(() => {
return window.localStorage.getItem("foo");
});
if (foo) {
console.log("LocalStorage foo exists:", foo); // State persisted
} else {
console.log("LocalStorage foo does not exist, this is the first run");
}
// Session state is maintained by the Session API across connections
await page.evaluate(() => {
localStorage.setItem("foo", "bar"); // This will persist for future connections
});
// Session remains active even after closing browser connection
await browser.close(); // Session continues running until TTL expires
import asyncio
from playwright.async_api import async_playwright
# Use the WebSocket URL returned from session creation
browser_wse_endpoint = 'wss://production-sfo.browserless.io/e/53...21/session/connect/b9..7b?token=25df...'
async def main():
async with async_playwright() as p:
# Connect to the existing session
browser = await p.chromium.connect_over_cdp(browser_wse_endpoint)
context = browser.contexts[0] # Use existing browser context
page = await context.new_page()
await page.goto("https://example.com")
print(await page.url())
# Check if session state persists from previous connections
foo = await page.evaluate("window.localStorage.getItem('foo')")
if foo:
print('LocalStorage foo exists:', foo) # State persisted
else:
print('LocalStorage foo does not exist, this is the first run')
# Session state is maintained by the Session API across connections
await page.evaluate("window.localStorage.setItem('foo', 'bar')") # This will persist
# Session remains active even after closing browser connection
await browser.close() # Session continues running until TTL expires
asyncio.run(main())
Next Steps
- Managing Sessions - Learn how to connect to and manage existing sessions
- Closing Sessions - Understand session cleanup and termination